News
LATEST NEWS
- 01Application of ceramic plunger pump
- 02The structure and principle of ceramic pumps
- 03Alumina ceramic properties
- 04Ceramic and stainless steel differences of three-cylinder plunger pump
- 05Common faults of ceramic plunger pump
- 06Energy-saving ceramic piston pump
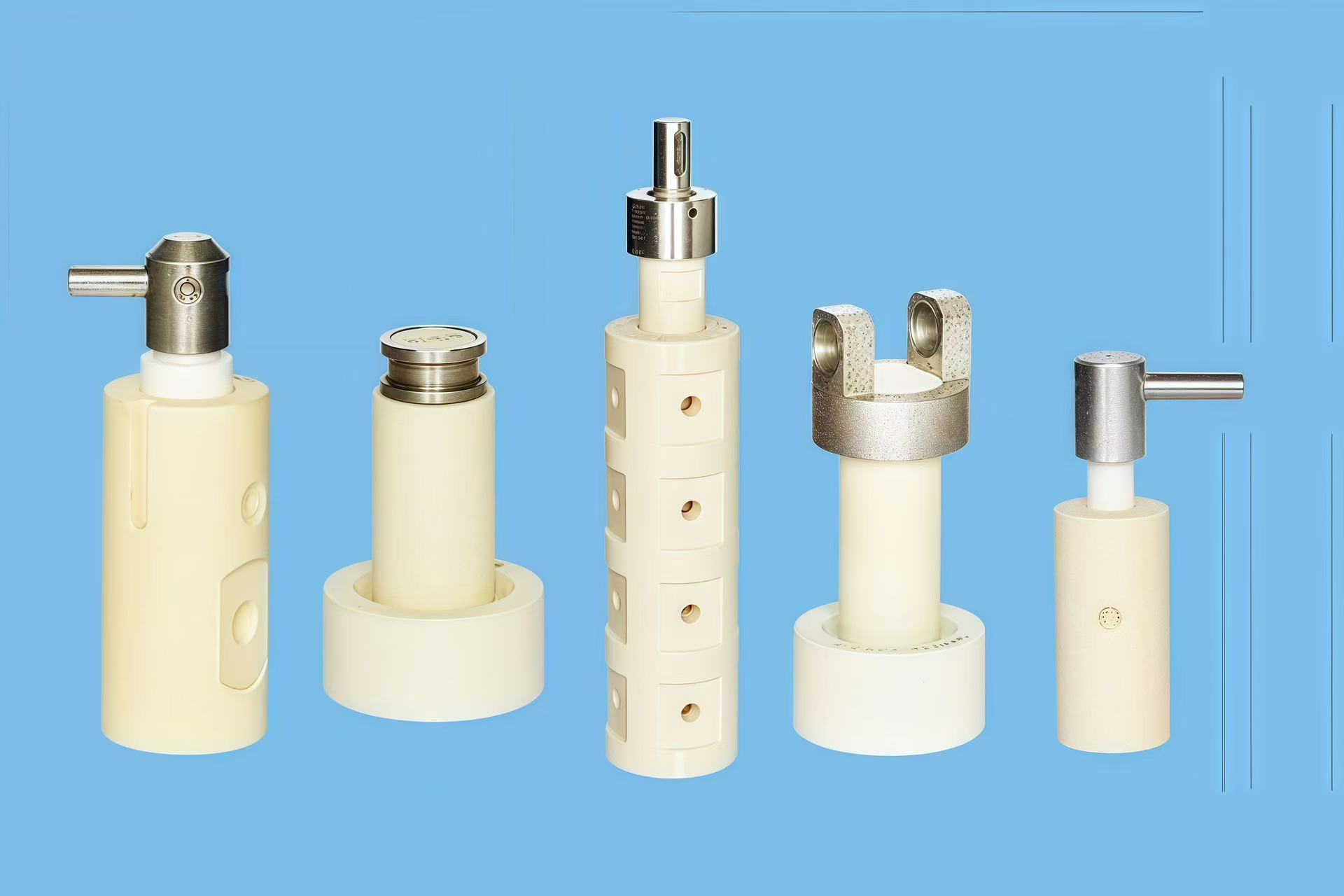
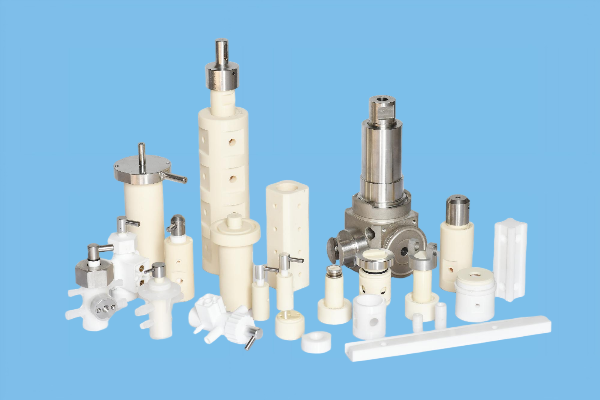
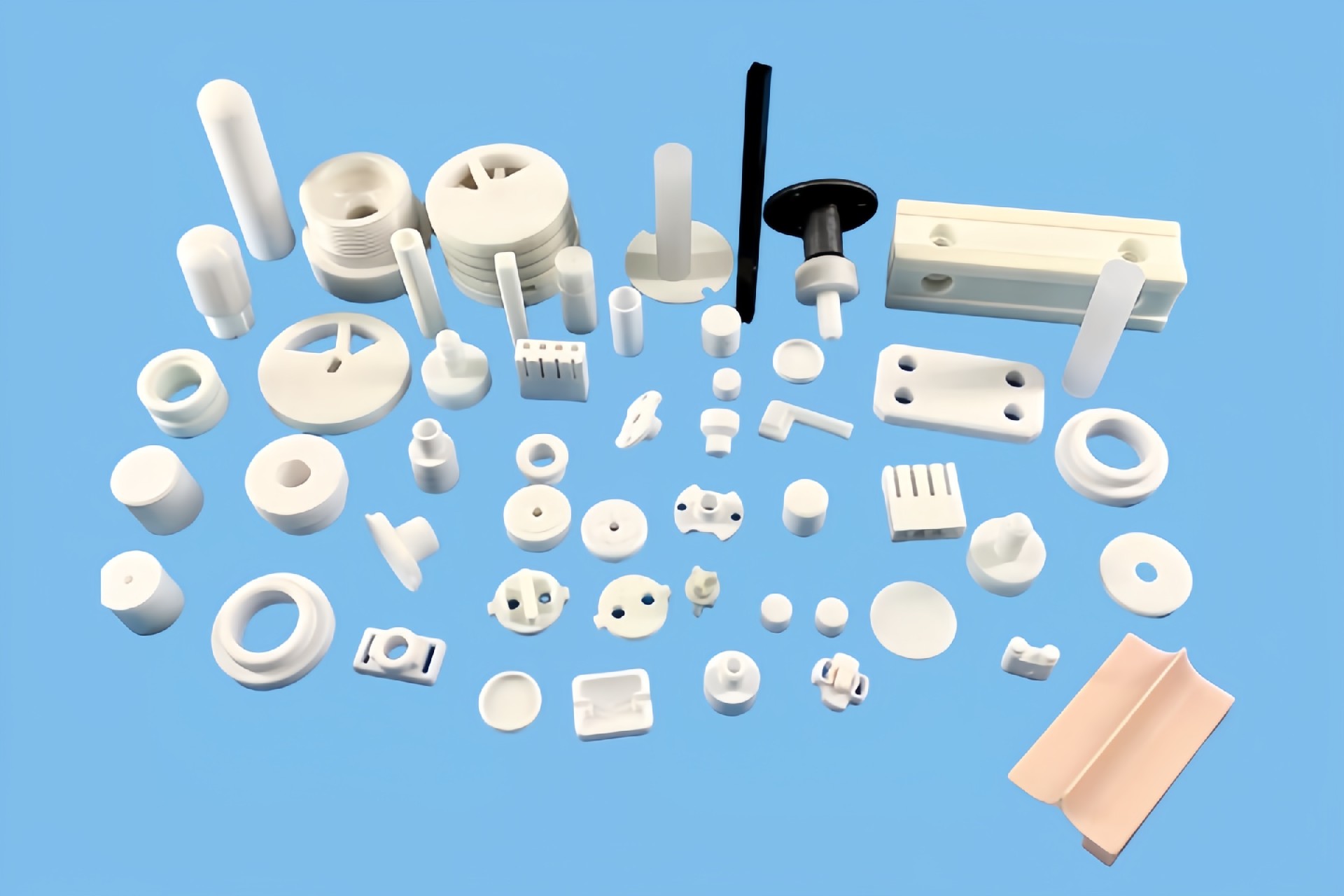
- 07Ceramic Plunger Pump Parts
- 08Ceramic slurry plunger pump
- 09Hydraulic ceramic piston pump
- 010Working principle of ceramic plunger pump

Address:1st Floor, Zixiang Road, Pingshan District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province
Zip Code: 518100
Phone: +86 13410681808
E-mail:glzmdy@163.com
News
HOMENews
Centrifugal pump; The most common centrifugal pump failure
2025-12-30 08:24:12 View:117Centrifugal pump failures consistently pose a significant risk in industrial operations, not only potentially damaging the equipment itself but also incurring substantial production losses due unscheduled downtime and emergency repairs. Establishing and consistently implementing a robust preventive maintenance program is one of the key strategies to circumvent such issues. Nevertheless, unforeseen are challenging to prevent entirely. Therefore, it is imperative to be prepared for swift diagnosis and timely response to effectively control the impact of faults and prevent pump system issues from escalating further.
The most common centrifugal pump faults
Firstly, let's sort out a few types of faults in the centrifugal pump system. Accurate identification of fault characteristics is the key premise for quickly locating the root cause of the problem.
1.creased flow rate: This is usually caused by impeller wear, blockage, seal leakage, or flow passage obstruction.
2. Overheating of equipment: It is to focus on checking the lubrication condition, whether the cooling system operates normally, or whether there is abnormal friction.
3. Abnormal vibration: Possible causes include mis of the shaft, cavitation, imbalance of the impeller (rotor), or bearing wear.
4. Cavitation phenomenon: When the local pressure is too, it can cause the formation of steam bubbles that burst instantly, damaging the pump body and/or impeller.
5. Abnormal noise: The appearance of impact friction sound is mostly related to misalignment of parts, cavitation, or bearing wear.
6. Fluid leakage: This is generally caused by seal failure or structural to the equipment.
7. Fluid contamination: This usually occurs due to seal failure, allowing external contaminants to enter the system internally.
8 Motor faults: Motor problems may trigger pump faults, and abnormal operation of the pump may also adversely affect the motor.
9. Decreased energy efficiency: Various problems the pump (such as wear of the wear ring, blockage of the flow passage, etc.) may be manifested as a decrease in the operating efficiency of the system.
10. Filling failure: Inlet air in the suction pipeline or insufficient inlet liquid level are common causes.
Steps for troubleshooting centrifugal pump
When a centrifugal pump exhibits the above faults, it is recommended to follow the following five key steps for systematic troubleshooting and handling:
1. Ident the fault phenomenon
All diagnosis begins with the accurate identification of the phenomenon. The system may exhibit multiple faults simultaneously or only show a specific abnormality. A clear definition the problem's manifestation is the premise for tracing the root cause and determining the target for maintenance or replacement.
2. Observe equipment operation
The more you are with the equipment, the higher the troubleshooting efficiency. If slight changes in performance during routine operation can be detected early, there is an opportunity to intervene and handle them before deteriorate. Even if the fault has already occurred, observing the operating status can still assist in determining the nature and source of the problem.
3. Implement special
When the source of the fault is not intuitive, it is necessary to use special tests and key parameter measurements to locate the abnormal link. This process often relies on experience and is also the core of accurate diagnosis.
4. Check key components
Most pump faults can be attributed to several key components, such as mechanical seals, alignment, impellers, bearings, valves, lubrication systems, and driving motors, etc. If there is no clear direction, it is recommended to start the investigation from these components
5. Apply intelligent monitoring technology
Today, monitoring, control, and predictive maintenance technologies have reached a high degree of maturity, capable of capturing precise performance data real-time. AI tools can analyze information instantly, identifying subtle anomalies; some sensors can even directly locate the source of the fault. The long-term return on investment in modern technology will be significant if it can ultimately save significant amounts of time and cost.