News
LATEST NEWS
- 01Application of ceramic plunger pump
- 02The structure and principle of ceramic pumps
- 03Alumina ceramic properties
- 04Ceramic and stainless steel differences of three-cylinder plunger pump
- 05Common faults of ceramic plunger pump
- 06Energy-saving ceramic piston pump
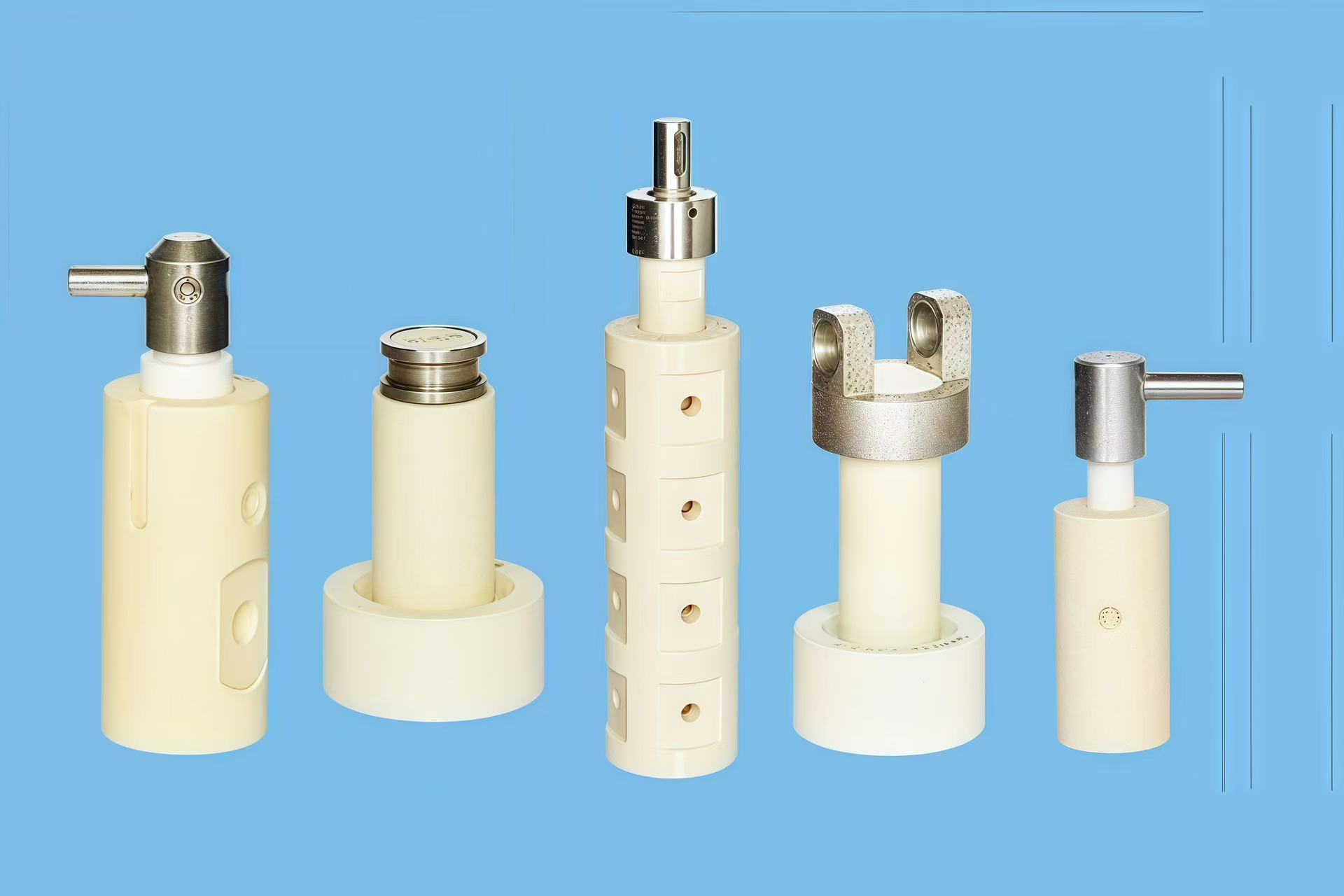
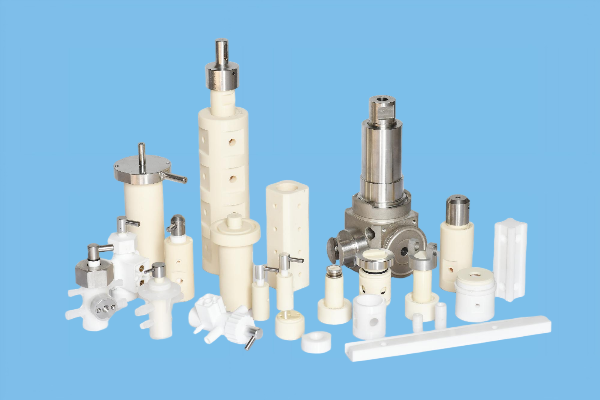
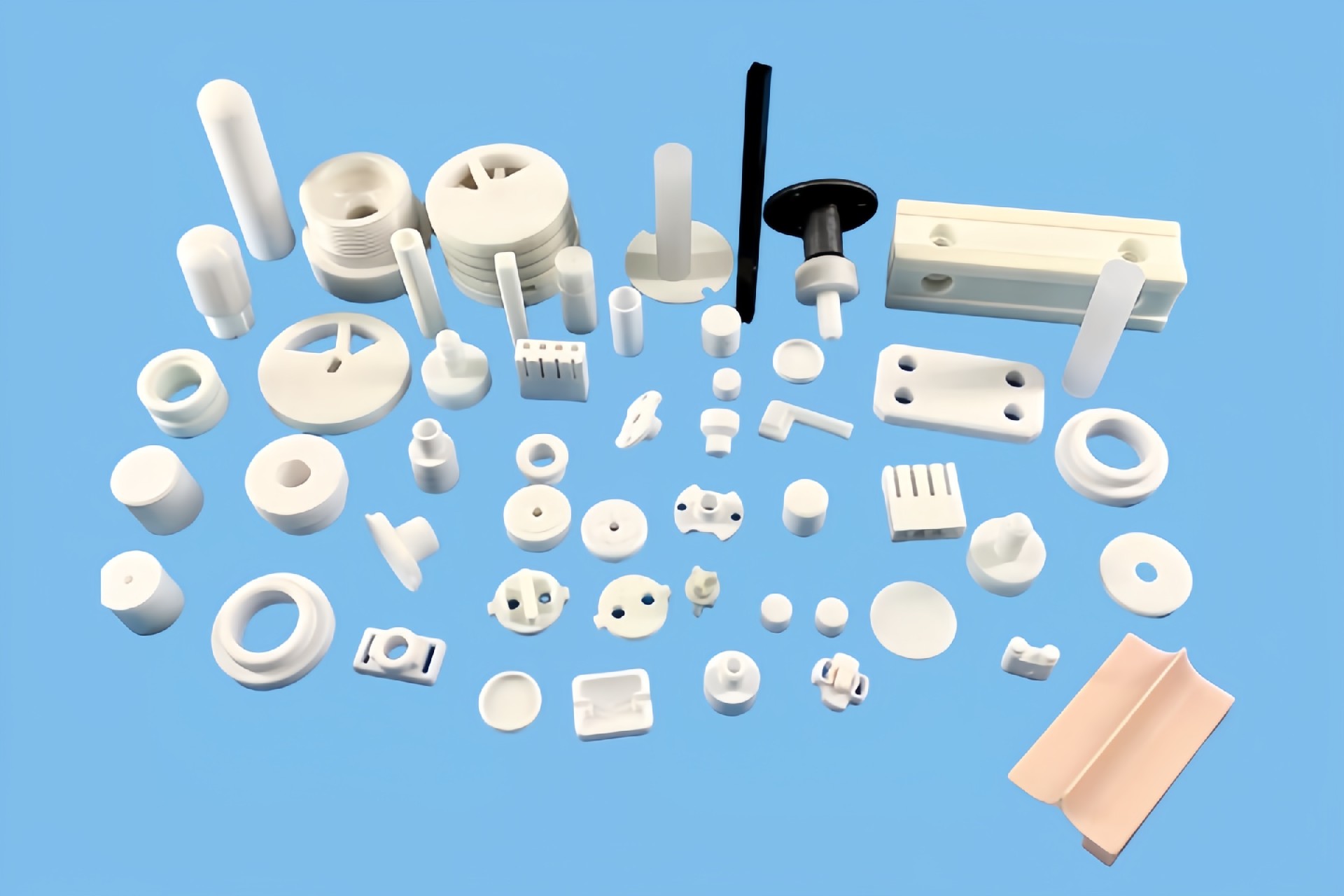
- 07Ceramic Plunger Pump Parts
- 08Ceramic slurry plunger pump
- 09Hydraulic ceramic piston pump
- 010Working principle of ceramic plunger pump

Address:1st Floor, Zixiang Road, Pingshan District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province
Zip Code: 518100
Phone: +86 13410681808
E-mail:glzmdy@163.com
News
HOMENews
What is the difference between a check valve and a non-return valve?
2025-12-31 08:19:22 View:131This is a very common engineering and fluid system problem. Simply put, check valves and non- valves are identical; they are just two different names for the same type of valve.
You can understand it as the relationship between "potato" and "potato.
Let me explain it in detail for you below, and why there are two names, and in what situations there may be subtle contextual differences.
Core: exactly the same
Chinese name: check valve, non-return valve, backflow preventer
Core function: allows the fluid (liquid or gas) flow in only one direction and completely prevents reverse flow.
Detailed explanation of functions
The working principle of this valve relies on the pressure of the fluid itself automatically open or close.
Forward flow: When the fluid flows into the inlet port, the pressure overcomes the resistance such as the gravity and spring force of the valve (or valve core), and the valve is pushed open to form a passage for flow.
Reverse flow: When the fluid attempts to flow reversely or the inlet pressure is lower than the outlet pressure, the valve disc is quickly closed under the action of the reverse fluid pressure, spring force, or its own gravity, sealing the flow passage thus preventing backflow.
Why are there two names?
This is mainly due to historical habits and different emphases in various application fields.
Check valve
Source: This name is more traditional and is more commonly used in general machinery, HVAC, water supply and drainage, and hydraulic engineering.
Focus The name emphasizes its core function of "preventing backflow". For example, installing a check valve at the outlet of a water pump is to prevent water from flowing back and the pump impeller when the pump is stopped.
Check valve
Source: This name is more popular in modern industrial fields such as hydraulic systems, pneumatic, automotive engineering, and aerospace.
Focus: The name more intuitively describes its "uni-directional conduction" characteristics. In these systems, precise control of flow direction of the oil or gas is crucial.
Common types
Regardless of whether they are called "check valve" or "non-return valve" they all have the following common types, with different structures and suitable for different occasions:
Swivel Check Valve: The valve disc rotates like a door around the shaft open and close. Suitable for pipelines with relatively constant flow.
Lift Check Valve: The valve disc moves up and down vertically to the valve seat like a pist. With good sealing performance, but relatively large flow resistance, it is suitable for high-pressure small-diameter occasions.
Ball Check Valve: Uses a sphere the valve disc, with a simple structure and good sealing performance, often used for small flow or viscous fluids.
Diverter Check Valve: The structure is similar to diverter valve, and the valve disc is a disk. Suitable for high-flow, low-pressure difference occasions.
Plug Check Valve: The valve disc is along the pipeline axis direction to open and close, with extremely small flow resistance and fast closing speed, often used in occasions requiring quick response and low pressure drop (such as oil gas pipelines).
Conclusion:
In daily communication or technical selection, you can consider "check valve" and "non-return valve" as completely synonymous. The choice of which word to use depends more on the habits of your industry and the background of your communication partner. Their functions, working principles, and structural types are all the.